special test to diagnose acetabular labral tears|acetabular labral tear lab tests : agencies To diagnose a hip labral tear your doctor will review your medical history, conduct a physical exam, and order one or more imaging tests. As a first step toward making a diagnosis, your doctor will ask about your symptoms . Resultado da 9 de nov. de 2021 · Bookmakers, betting shops in Liechtenstein: legal since 2010, operators require a licence. Online sports betting in Liechtenstein: legal since 2010, operators require a licence . Sports betting is legal in Liechtenstein and the most popular sport to bet on is football. The only .
{plog:ftitle_list}
web77 sec Suzie Slut - 56.5k Views - 1080p. Comendo o cu da policial gostosa - suzie slut 10 min. 10 min Gostosas Video - 654k Views - 1440p. Não sei transar é contratei suzie slut para uma foda 3 min. 3 min Gostosas Video - 1M Views - 1440p. GOZEI IGUAL UM CAVALO NA CARA DE MINHA MULHER 4K - JOTA E SUZIE SLUT 4 min.
The gold standard for diagnosing an acetabular labral tear is considered to be direct visualization by arthroscopy. A medical physician may wish to utilize less invasive measures to make a diagnosis such as MR arthrography and or intra-articular hip injections with anesthetic.
The McCarthy Test is a clinical test used in the diagnosis of a hip labral tear. The .An acetabular labral tear can cause pain if the labrum is torn, frayed, or damaged. . To diagnose a hip labral tear your doctor will review your medical history, conduct a physical exam, and order one or more imaging tests. As a first step toward making a diagnosis, your doctor will ask about your symptoms .An acetabular labral tear can cause pain if the labrum is torn, frayed, or damaged. Labral tears cause groin pain or pain in the anterior side of the hip, and less commonly buttock pain. [1] This mechanically induced pathology is .
This paper aims to assess the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and latest evidence-based treatment of acetabular labral tears. The acetabular labrum contributes to the stability .
acetabular tear ultrasound
acetabular tear diagnosis
Clinical examination should consider lumbopelvic and extra-articular pathologies in addition to intra-articular pathologies when assessing for the source of symptoms and . Diagnosis generally requires an MR arthrogram of the hip joint in question. Treatment is a nonoperative trial to include NSAIDs, rest and physical therapy. Arthroscopic labral debridement versus repair is indicated for patients . In summary, both the impingement test and MRA have high sensitivity and accuracy for the diagnosis of acetabular labral tears. Hip arthroscopy is a minimally invasive . They can check for arthritis and for structural problems. A magnetic resonance arthrography (MRA) can provide detailed images of your hip's soft tissues. magnetic .
A healthcare provider will diagnose a hip labral tear with a physical exam and some tests. They’ll examine your hip and ask you about your symptoms. Tell your provider when you first noticed . The acetabular labrum contributes to the stability of the hip joint by increasing the articular surface of the joint and the depth of the acetabulum and creating a suction-seal effect on the femoral head [1,2,3,4].While acetabular labral tears are prevalent in both symptomatic and asymptomatic individuals, the prevelence is slightly higher in symptomatic individuals (62% . What are hip labral tear symptoms? The most common symptoms of a labral tear in your hip include: Hip pain (especially when you bend, move, exercise or play sports). . A healthcare provider will diagnose a hip labral tear with a physical exam and some tests. They’ll examine your hip and ask you about your symptoms. Tell your provider when .
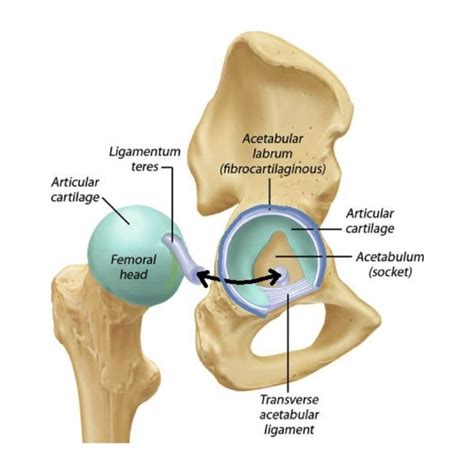
Hip Labral Tear Symptoms. . If the labral tear diagnosis is still unclear after these tests, your doctor may recommend an ultrasound-guided injection with a painkiller. If it relieves pain, then it is likely that the cause is a labral tear. . The hip labrum may become torn or even detached from the acetabular socket for a variety of reasons. Hip labral tear causes. . Diagnosis. Labral tears are difficult to diagnose, partially because of the many muscles and other structures that are near the hip joint. They are often misdiagnosed as common groin strains and it is not uncommon for .
acetabular labral tear weight
Acetabular labrum tears (ALT) are present in 22–55% of individuals with hip or groin pain. Tears can occur as a result of trauma or degeneration and are markedly associated with femoral acetabular morphological variations. An ALT can lead to biomechanical deficiencies and a loss of stability to the coxafemoral joint due to the labrum serving as a stabilising structure of this joint. .Introduction [edit | edit source]. Traditionally Orthopaedic Special tests were used to assist in the diagnostic process by implicating specific tissue structures that are either dysfunctional, pathological, or lack structural integrity, confirming the findings from the physical assessment and providing a tentative diagnosis. Special testing is generally performed following a full .
Injury to or dislocation of the hip joint — which can occur during car accidents or from playing contact sports such as football or hockey — can cause a hip labral tear. Structural problems. Some people are born with hip issues that can accelerate wear and tear of the joint and eventually cause a hip labral tear. Labral tears can be difficult to diagnose because many hip injuries cause similar symptoms. They’re often misdiagnosed for groin strains, according to the Hospital for Special Surgery .Purpose of Review This paper aims to assess the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and latest evidence-based treatment of acetabular labral tears. Recent Findings The acetabular labrum contributes to the stability of the hip. Labral tears may lead to significant pain and disability, although many are asymptomatic. Labral tears may cause a popping, catching, or clicking sound associated with activities such as dance, gymnastics, hockey, basketball, and soccer. 2, 5, 9 Physical examination for labral tears .
strong cobb tester
A PT, an OS, and two ORs independently performed history and examinations with the emphasis of diagnosis on the results of six special tests. Results: Thirty-two of 37 individuals (86%) had labral tears to the hip at arthroscopy. Analysis of agreement between clinical diagnosis and intra-operative findings of a labral tear produced a CDA of 85. .Acetabular labrum tears (ALT) are present in 22-55% of individuals with hip or groin pain. . Examination of acetabular labral tear: a continued diagnostic challenge Br J Sports Med. 2014 Feb;48(4) :311-9 . clinical examination and special test findings that are unique to the condition. Imaging methods such as MRI, CT and ultrasonography . Objective: To review the literature regarding diagnosis and treatment of labral tear. Data sources: A systematic search was performed in PubMed using various search terms and their combinations including hip, labrum, acetabular labral tear, arthroscopy, diagnosis, and anatomy. Study selection: For each included study, information regarding anatomy, function, .This statement summarises and appraises the evidence on diagnostic tests and clinical information, and non-operative treatment of femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) syndrome and labral injuries. We included studies based on the highest available level of evidence as judged by study design. We evaluated the certainty of evidence using the Grading of .
Labral tears are usually caused by overuse or injury and commonly accompany other injuries to the shoulder. View our orthopaedic doctors who specialize in diagnosing and treating shoulder labral tears. Types of Labral Tears of the . All labral tears were confirmed by arthroscopy, demonstrating that the impingement test is extremely accurate in the diagnosis of labral tears. The McCarthy test for acetabular labral tears 7 was developed earlier than the FADER and FABER tests. Although a positive McCarthy test is not very common in labral lesions, it has a high specificity.Superior labral anterior posterior (SLAP) tears are injuries of the glenoid labrum. They involve the superior glenoid labrum, . The physical examination: A combination of two sensitive tests and one specific test is useful to diagnose .
The validity and accuracy of clinical diagnostic tests used to detect labral pathology of the hip: a systematic review. Manual therapy. 2011 Aug 1;16(4):318-26. Manual therapy. 2011 Aug 1;16(4):318-26.acetabular impingement, labral tears, and gluteus medius tendon tears typically have good surgical outcomes, advanced imaging and/or early referral may improve patient outcomes. (Am Fam Physician .
A 2011 study on acetabular labral tears looked at MRI and MRA accuracy. Researchers evaluated 19 published papers that covered 881 hips. . (sometimes called “special tests” for hip labral tears). . The researchers used patient symptoms and MRI to see if they could find a correlation between symptoms, the imaging findings, the injections . Acetabular labral tears represent the most common cause for mechanical hip symptoms – in a recent study, they were found to be the cause of groin pain in more than 20% of athletes presenting with groin pain. Acetabular Labral Tear Classification. Labral tears can be classified according to location, etiology, and type: Location:Impingement Test. As part of the physical examination, your doctor will likely conduct the impingement test. For this test, your doctor will bring your knee up toward your chest and then rotate it inward toward your opposite shoulder. If this re-creates your hip pain, the test result is positive for impingement.A Patient's Guide to Labral Tears of the Hip Introduction Acetabular labrum tears ( labral tears) can cause pain, stiffness, and other disabling symptoms of the hip joint. The pain can occur if the labrum is torn, frayed, or damaged. Active adults between the ages of 20 and 40 are affected most often, requiring some type of treatment in order .
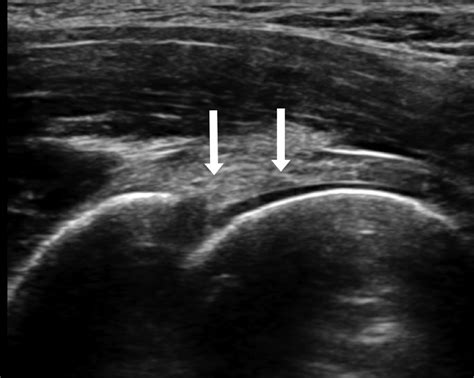
The impingement test is helpful in identifying acetabular labral tears. If this test is negative and if a labral tear is still suspected, ultrasound can reliably diagnose most tears of the acetabular labrum. MR arthrography is indicated in cases where .To diagnose hip labral tears, NYU Langone doctors take a medical history, perform a physical exam, and use the newest imaging techniques. Read more. . Our doctors frequently recommend one or more diagnostic imaging tests to confirm the presence of a hip labral tear or other joint damage. These tests are painless and take place at NYU Langone.acetabular labral tears. Once considered an uncom-mon entity, labral tears as a source of symptoms and functional limitation in the hip region have become more recognized. A labral tear was arthroscopically identified in 90% of individuals with mechanical hip symptoms.29,55 However, isolated labral tears occur in
acetabular labral tear treatment
The later section on cam impingement discusses the use of imaging to diagnose acetabular labral tears and associated bony abnormalities. . pain provocation maneuvers before and after diagnostic intraarticular injection to determine the validity of the tests in the diagnosis of intraarticular hip disorders. If pain decreased greater than or .
Imóveis - Franca, SP | OLX. Ir para o menu principal Ir para .
special test to diagnose acetabular labral tears|acetabular labral tear lab tests